GEOGRAFI TINGKATAN 3 (Nota 19)
BAB 11: KITAR SEMULA
The 4-in-1 Recycling Program
Before January 1997, although the Waste Disposal Act had required manufacturers and importers to recycle Regulated Recyclable Waste (RRW), the collection channels were not coordinated, so the collection rate was low. Furthermore, manufacturers and importers did not invest in recycling facilities installation due to underdeveloped regulations and incentives. In1997, Environmental Protection Administration Taiwan (EPAT) created the “4-in-1 Recycling Program to better connect all parties involved in RRW collection channels, including community residents, recyclers and collectors, local governments, and the newly established Recycling Fund. Through the incentives associated with the Fund, the 4-in-1 Recycling Program has increased recycling rates and reduced the amount of solid waste sent for disposal. The structure of the 4-in-1 Recycling Program is illustrated in Figure 1.
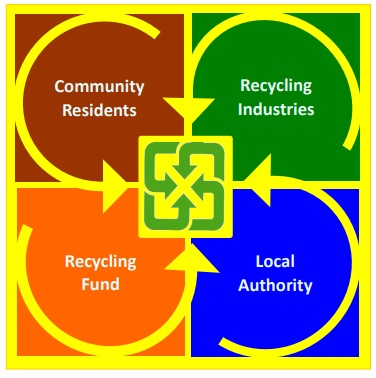
Figure 1 The structure of the 4-in-1 Recycling Program
Components of the 4-in-1 Recycling Program
1. Community Residents
Community residents make up the foundation of the 4-in-1 Recycling Program. Residents who deposit their waste at local collection points serviced by municipal collection teams must separate their recyclable, non-recyclable, and organic wastes. In addition to community residents, there are many citizen groups such as Tsu-Chi Foundation (a Buddhist organization), Homemakers United Foundation, and Conservation Mothers Foundation that work to increase recycling in communities and schools. These groups conduct recycling education programs, collect RRW for donation and reuse, and collect RRW for sale to recyclers. As of 2011, there were a total of 3,200 communities and 3,500 schools carrying out recycling. Through requirements and voluntary actions, RRW collection points have been installed in public places such as national parks, scenic spots, public transportation stations, as well as chain stores and supermarkets. These expanded collection channels make it convenient for citizens to send RRW for collection and recycling.
2. Recycling Industries
Private recyclers and collectors buy waste materials, including waste electric and electronic equipment (WEEE), from residents, communities, commercial enterprises and others in order to recover commodities from these wastes and generate revenue in the process.
3. Local Authorities
Municipalities and local governments organize municipal collection teams to collect RRW and other wastes from community collection sites. They sell RRW and other municipal solid waste (MSW) of value to private recyclers and give a portion of the income back to the local government in order to fund grants for community waste collection sites.
4. Recycling Fund
The Recycling Fund is the most important aspect of the 4-in-1 Recycling Program because it subsidizes municipal RRW collection as well as private collectors and recyclers who meet EPAT’s environmental and safety standards. Under the 4-in-1 Recycling Program, manufacturers and importers of new RRW products, including electrical and electronic equipment, are required to pay fees to EPAT depending on the quantity of items they put on the market. These fees feed into the Recycling Fund, which is managed by RFMB. Currently the recycling fund collects NT$7,000,000,000 (NT$7 Billion) per year from manufacturers and importers, which is distributed to trust funds and special income funds. The trust funds are used to subsidize private collectors and recycling enterprises that meet EPAT standards. Special income funds are dedicated to education, research and development, auditing, grants for municipalities and citizen groups, and administration of the 4-in-1 Recycling Program. The Recycling Fund has greatly advanced recycling in Taiwan. For example, money from the nonprofit fund been used to purchase more than 1,300 recycling vehicles for municipalities since 1998 so that collection of recyclables can be carried out more than twice per week. Money from the special income fund has also financed 273 storage facilities for 326 municipal collection squads since 1998.

(Sumber: https://goo.gl/mFnVNF)